Introduction to renv
SAFEHR Learning session
Milan Malfait
2025-02-24
Overview of renv
What is renv?
- A package for managing project-specific R environments
- Similar to virtual environments in Python (e.g.,
venvorconda)
Key Features
- Isolated library paths for each project
- Portable: cross-platform sharing of environments
- Reproducible: ensures consistent package versions
Why use renv?
- Challenges of dependency management in collaborative projects.
- Ensuring reproducibility across different systems and over time.
- Avoiding conflicts between package versions.

The renv workflow
The renv workflow
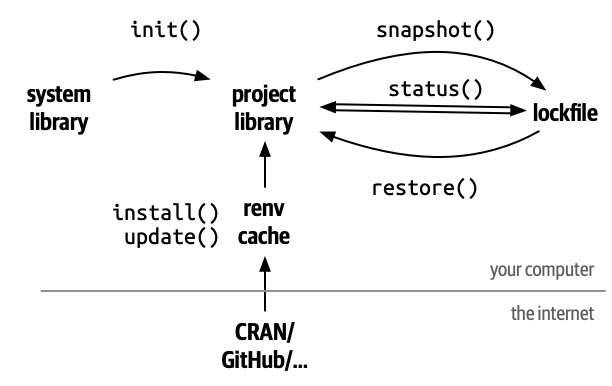
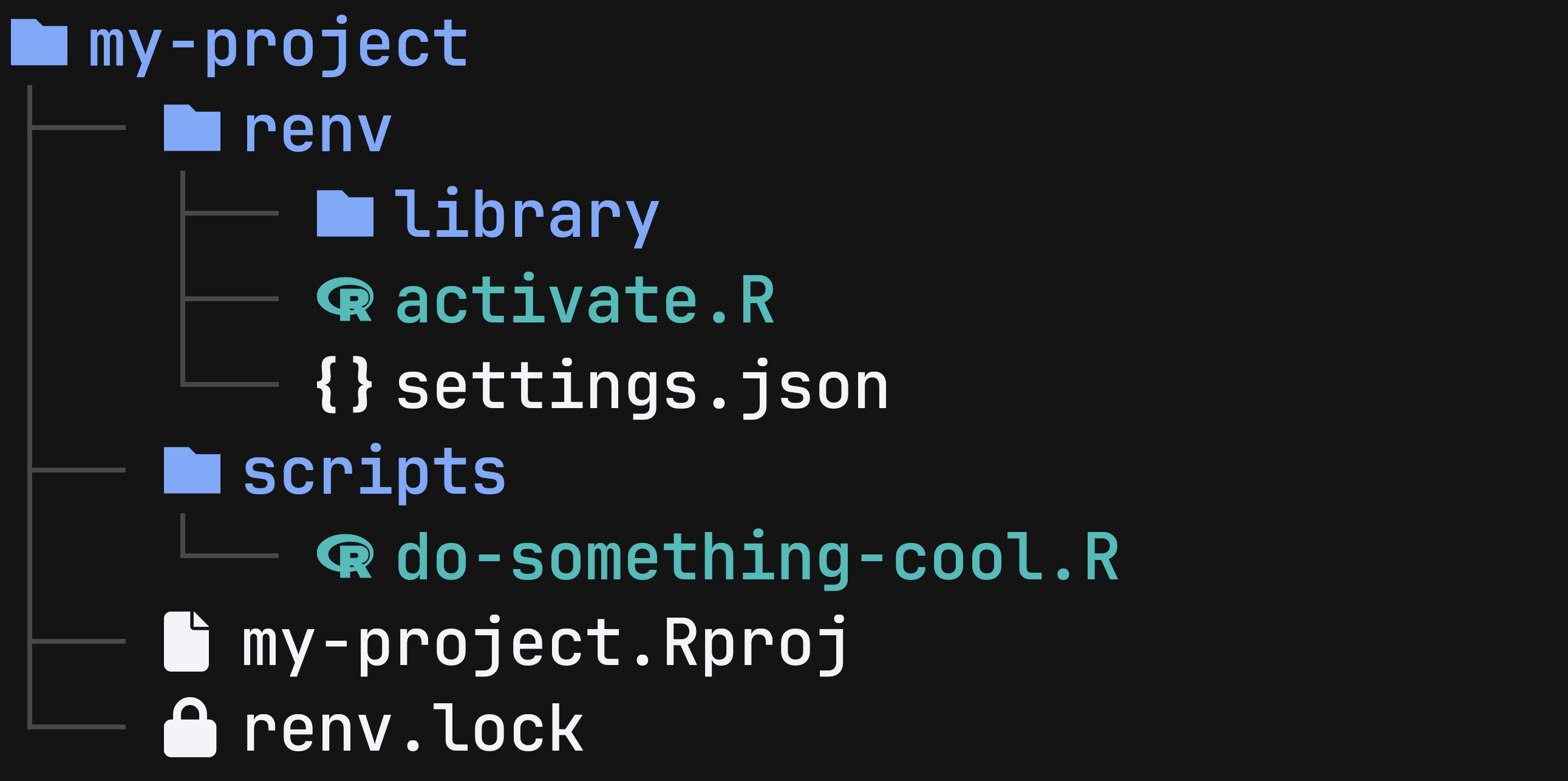
Setting Up renv in a Project
Recording the Environment
Recording the Environment
# On the console
renv::snapshot()
#> The following required packages are not installed:
#> - dplyr
#> Packages must first be installed before renv can snapshot them.
#> Use `renv::dependencies()` to see where this package is used in your project.
#>
#> What do you want to do?
#>
#> 1: Snapshot, just using the currently installed packages.
#> 2: Install the packages, then snapshot.
#> 3: Cancel, and resolve the situation on your own.
#>
Selection:Recording the Environment
# On the console
renv::snapshot()
Selection: 2
#> The following package(s) will be installed:
#> - cli [3.6.4]
#> - dplyr [1.1.4]
#> - fansi [1.0.6]
#> - generics [0.1.3]
#> - glue [1.8.0]
#> - lifecycle [1.0.4]
#> - magrittr [2.0.3]
#> - pillar [1.10.1]
#> - pkgconfig [2.0.3]
#> - R6 [2.6.1]
#> - rlang [1.1.5]
#> - tibble [3.2.1]
#> - tidyselect [1.2.1]
#> - utf8 [1.2.4]
#> - vctrs [0.6.5]
#> - withr [3.0.2]
#> These packages will be installed into "~/test/sandbox/my-project/renv/library/macos/R-4.4/aarch64-apple-darwin20".Recording the Environment
# On the console
renv::snapshot()
Selection: 2
#> The following package(s) will be installed:
#> - dplyr [1.1.4]
#> These packages will be installed into "~/test/sandbox/my-project/renv/library/macos/R-4.4/aarch64-apple-darwin20".
#> # Installing packages --------------------------------------------------------
#> ...
#> # CRAN -----------------------------------------------------------------------
#> ...
#> - dplyr [* -> 1.1.4]
#> ... more dependencies
Do you want to proceed? [Y/n]:Recording the Environment
The lockfile
The lockfile
Restoring the Environment
Updating Packages
renv::update()
#> - Querying repositories for available binary packages ... Done!
#> - Querying repositories for available source packages ... Done!
#> - Checking for updated packages ... Done!
#> The following package(s) will be updated:
#>
#> # CRAN -----------------------------------------------------------------------
#> - class [7.3-22 -> 7.3-23]
#> - foreign [0.8-87 -> 0.8-88]
#> - KernSmooth [2.23-24 -> 2.23-26]
#> - MASS [7.3-61 -> 7.3-64]
#> - Matrix [1.7-1 -> 1.7-2]
#> - nlme [3.1-166 -> 3.1-167]
#> - nnet [7.3-19 -> 7.3-20]
#> - rpart [4.1.23 -> 4.1.24]
#> - spatial [7.3-17 -> 7.3-18]
#> - survival [3.7-0 -> 3.8-3]renv will update the renv.lock file in this case.
Updating packages
Always good to run
and make sure everything is as it should be
Don’t forget to git commit changes to renv.lock!
Advanced Features and Best Practices
Recording a specific version of a package
Only do this when you have a compelling reason to do so
Good to know
- Use
.renvignoreto exclude files fromrenvmanagement - Modify
renv/settings.jsonfor project-specific configurations - Using
renvin automated workflows for consistent environments
Gotchas and how to deal with them
- RESTART, RESTART, RESTART
- Get in the habit of regularly restarting your R session
- Learn those keyboard shortcuts!
- Although the regular install commands (
install.packages(),remotes::install_github()) should work withrenv, userenv::install()just to be sure
Can’t find a package
renv::snapshot()
#> The following required packages are not installed:
#> - omopcept
#> Packages must first be installed before renv can snapshot them.
#> Use `renv::dependencies()` to see where this package is used in your project.
#>
#> What do you want to do?
#>
#> 1: Snapshot, just using the currently installed packages.
#> 2: Install the packages, then snapshot.
#> 3: Cancel, and resolve the situation on your own.
#>
#> Selection:Can’t find a package
😭
Can’t find a package
Typical for GitHub packages, because renv only looks at CRAN repo by default
Fix by manually installing the package first and then snapshotting again.
🥳
Resources
Introduction to renv | https://milanmlft.github.io/talks/